1. Introduction
In the modern world, the computer has become an essential part of our daily life. Computers are widely used in education, business, banking, healthcare, communication, research, and entertainment. A computer is an electronic machine that helps us perform tasks quickly, accurately, and efficiently by processing data.
- Education
- Business
- Banking
- Healthcare
- Communication
- Research
- Entertainment
A computer is an electronic machine that helps us perform tasks quickly, accurately, and efficiently by processing data.
2. Definition of Computer
A computer is an electronic device that accepts data as input, processes it according to a set of instructions, and produces meaningful information as output.
In simple terms, a computer performs four basic operations:
- Input
- Processing
- Output
- Storage
3. Computer System Overview
- A computer is a machine that can be programmed to perform arithmetic and logical operations automatically.
- Modern computers execute programs, which enable them to perform a wide variety of tasks.
- Computers are made of hardware (physical components) and software (programs and instructions).
- Early electronic computers (1940s) were huge, required teams to operate, and were much slower than today’s computers.
- Today’s computers are faster, smaller, portable, and thousands of times more powerful.

4. History of Computer
- The development of computers began with Charles Babbage, a 19th-century English mathematics professor.
- He designed the Analytical Engine, which became the framework for modern computers.
- The first fully electronic computer was the Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC).
Father of Computer: Charles Babbage
5. Full Form of COMPUTER
| Letter | Full Form |
|---|---|
| C | Common |
| O | Operating |
| M | Machine for |
| P | Personal |
| U | Use for |
| T | Technology |
| E | Education (Entertainment) & |
| R | Research |
6. Types of Computers
6.1 Based on Principles of Operation
- Analog Computers:
- Operates on continuous values
- Results are approximate
- Deals with physical variables such as voltage, pressure, temperature, speed
- Digital Computers:
- Operates on binary numbers (0 & 1)
- Accurate and fast
- Well-suited for engineering, technology, research
- Special Purpose: Built for specific applications
- General Purpose: Can perform multiple tasks
- Hybrid Computers:
- Combines features of analog & digital
- Used in specialized tasks like ICU monitoring in hospitals
Difference between Analog Computers and Digital Computers
| S. No. | Analog Computers | Digital Computers |
| 1 | Its functions on physical analog system. | It functions on discrete numbers system. |
| 2 | The calculations in this system are primarily converted to equations and later converted into electrical signals. | The calculations in this system are converted into binary numbers (i.e., 1s and 0s). |
| 3 | To function, it requires physical analog. | To function, it requires discrete numbers. |
| 4 | It gives output in the form of ‘graph’. | It gives output in the form of discrete values. |
| 5 | Accuracy comparatively is less. | Accuracy is very high. |
| 6 | Performs at a low speed. | It performs at a very high speed. |
| 7 | Difficult to make changes, as it is less flexible. | It is highly flexible. |
| 8 | It has memory of low capacity. | It has memory of high capacity. |
| 9 | Its application is limited to certain applications. | Its application is applicable to a number of applications. |
| 10 | It is hardly applicable for the business applications. | It is very much suitable for the business applications. |
| 11 | It cannot process alpha-numeric data. | It can process alpha-numeric data. |
| 12 | It requires RF technology. | It requires IP networking. |
| 13 | Static channel assignment. | Automatic channels exist as required. |
6.2 Types of Computer (Based on Size and Capacity)
Computers can be classified into different types based on their size, performance, and processing power.
6.2.1 Super Computer
A Super Computer is the fastest and most powerful type of computer. It is capable of performing extremely complex calculations at very high speed.
Uses of Super Computer
- Weather forecasting
- Space research
- Nuclear research
- Scientific simulations
Examples
- PARAM (India)
- Fugaku (Japan)
Definition:
A supercomputer is a high-performance computer that can process trillions of instructions per second.

6.2.2 Mainframe Computer
A Mainframe Computer is a powerful computer used by large organizations to handle huge volumes of data and multiple users at the same time.
Uses of Mainframe Computer
- Banks and financial institutions
- Airline and railway reservation systems
- Government organizations
Definition:
A mainframe computer is a large-capacity computer designed to process and manage massive amounts of data for many users simultaneously.

6.3.3 Mini Computer
A Mini Computer is a medium-sized computer that is more powerful than a microcomputer but less powerful than a mainframe computer.
Uses of Mini Computer
- Small and medium businesses
- Colleges and research laboratories
Definition:
A minicomputer is a multi-user computer that provides moderate computing power and supports multiple users at the same time.

6.4 Based on Size
| Type | Description & Use |
|---|---|
| Micro Computer | Single-user, low speed and storage; includes PCs, laptops, portable computers |
| Mini Computer | Medium-sized, multi-user, departmental use; supports hundreds of users |
| Mainframe | Large computer for many users; used by banks, governments; high storage & speed |
| Workstation | High-performance standalone system; used for engineering, design, publishing |
| Super Computer | Extremely fast, high storage, scientific simulations, weather forecasting |
Portable Computers: PDAs, laptops, notebook computers
Personal Computers / Desktop: CPU, monitor, keyboard, mouse, hard disk
7. Characteristics of a Computer
A computer has several important characteristics that make it useful:
- SPEED: In general, no human being can compete to solving the complex computation, faster than computer.
- ACCURACY: Since Computer is programmed, so whatever input we give it gives result with accurately.
- STORAGE: Computer can store mass storage of data with appropriate format.
- DILIGENCE: Computer can work for hours without any break and creating error.
- VERSATILITY: We can use computer to perform completely different type of work at the same time.
- POWER OF REMEMBERING: It can remember data for us.
- NO IQ: Computer cannot work without instructions.
- NO FEELING: Computer does not have emotions, knowledge, experience, feeling.
8. Generations of Computer
The development of computers is divided into five generations based on the technology used.
Generations of Computer :- There are the following generations of computer.
Generation in computer terminology is a change in technology a computer is/was being used. Initially, the generation term was used to distinguish between varying hardware technologies. Nowadays, generation includes both hardware and software, which together make up an entire computer system.
There are five computer generations known till date. Each generation has been discussed in detail along with their time period and characteristics. In the following table, an approximate date against each generation has been mentioned, which are normally accepted.
Following are the main five generations of computers.
First Generation of Computers: – The period of first generation: 1946-1959. Vacuum tube based.
The period of first generation was from 1946-1959. The computers of first generation used vacuum tubes as the basic components for memory and circuitry for CPU (Central Processing Unit). These tubes, like electric bulbs, produced a lot of heat and the installations used to fuse frequently. Therefore, they were very expensive and only large organizations were able to afford it.
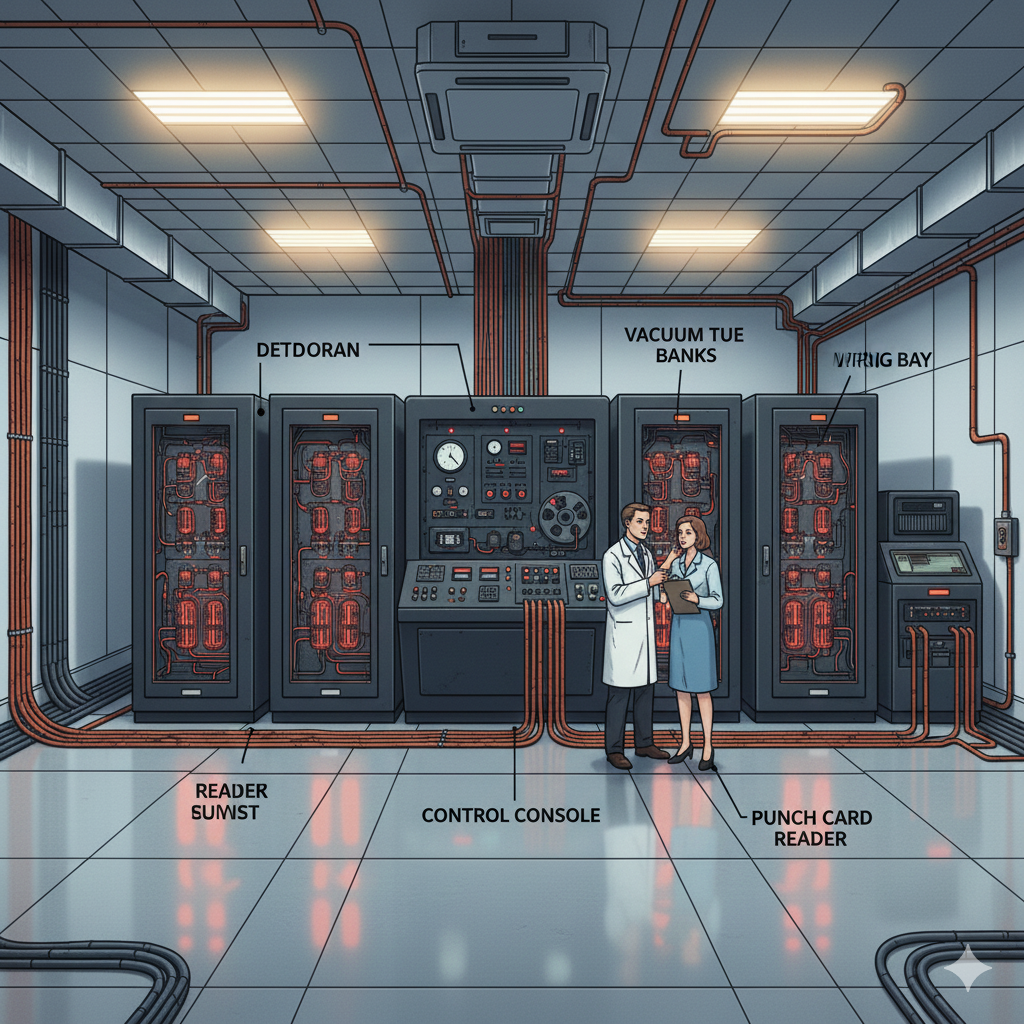
In this generation, mainly batch processing operating system was used. Punch cards, paper tape, and magnetic tape were used as input and output devices. The computers in this generation used machine code as the programming language.
The main features of the first generation are −
- Vacuum tube technology
- Unreliable
- Supported machine language only
- Very costly
- Generated a lot of heat
- Slow input and output devices
- Huge size
- Need of AC
- Non-portable
- Consumed a lot of electricity
Some computers of this generation were −
- ENIAC
- EDVAC
- UNIVAC
- IBM-701
- IBM-650
Second Generation of Computers: – The period of second generation: 1959-1965. Transistor based.
The period of second generation was from 1959-1965. In this generation, transistors were used that were cheaper, consumed less power, more compact in size, more reliable and faster than the first generation machines made of vacuum tubes. In this generation, magnetic cores were used as the primary memory and magnetic tape and magnetic disks as secondary storage devices.
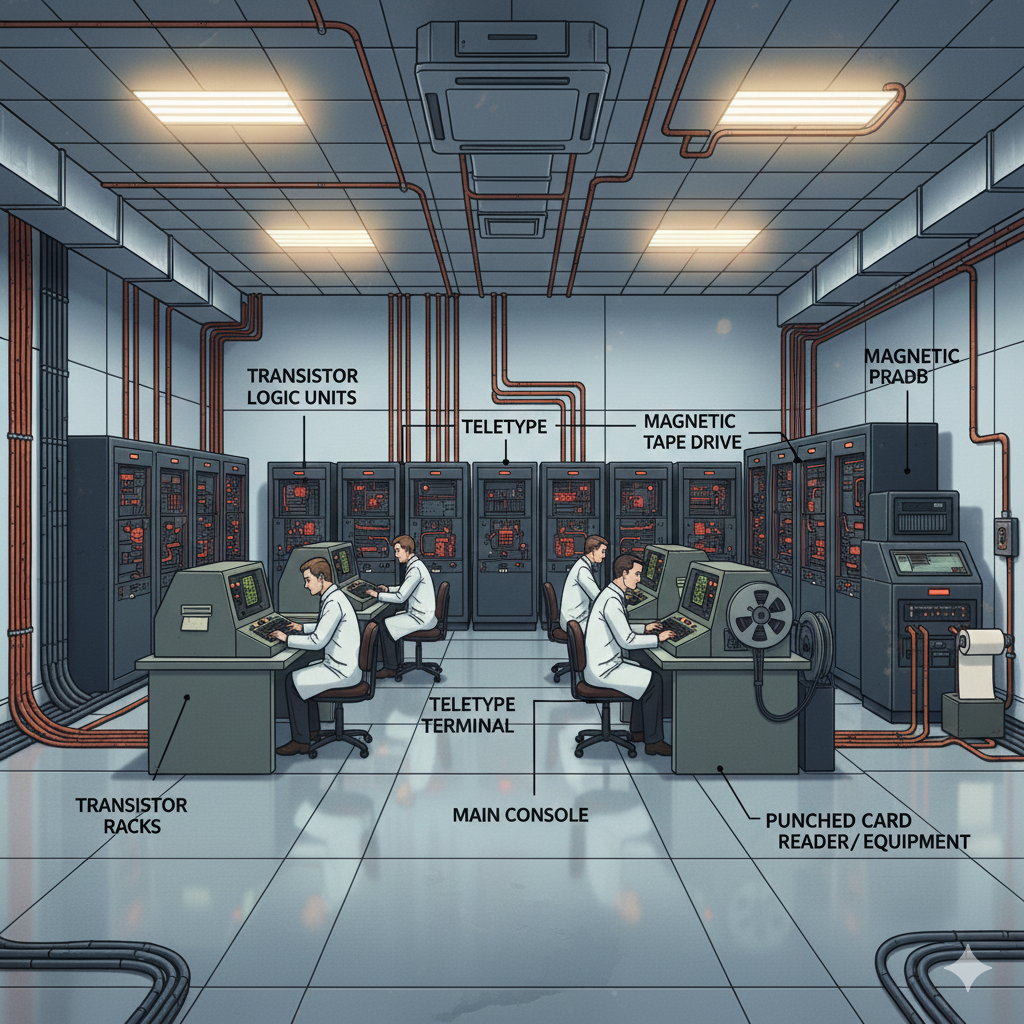
In this generation, assembly language and high-level programming languages like FORTRAN, COBOL were used. The computers used batch processing and multiprogramming operating system.
The main features of second generation are −
- Use of transistors
- Reliable in comparison to first generation computers
- Smaller size as compared to first generation computers
- Generated less heat as compared to first generation computers
- Consumed less electricity as compared to first generation computers
- Faster than first generation computers
- Still very costly
- AC required
- Supported machine and assembly languages
Some computers of this generation were −
- IBM 1620
- IBM 7094
- CDC 1604
- CDC 3600
- UNIVAC 1108
Third Generation of Computers: – The period of third generation: 1965-1971. Integrated Circuit based.
The period of third generation was from 1965-1971. The computers of third generation used Integrated Circuits (ICs) in place of transistors. A single IC has many transistors, resistors, and capacitors along with the associated circuitry.
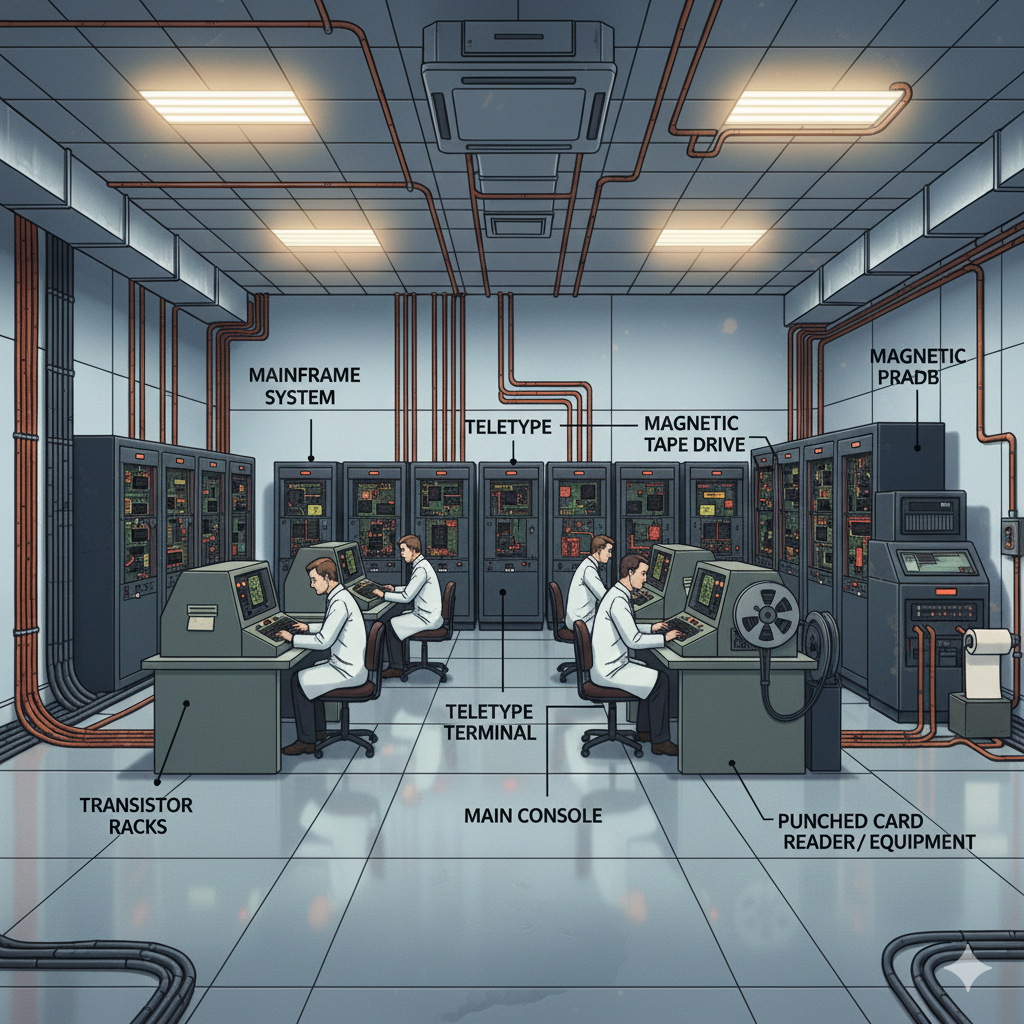
The IC was invented by Jack Kilby. This development made computers smaller in size, reliable, and efficient. In this generation remote processing, time-sharing, multiprogramming operating system were used. High-level languages (FORTRAN-II TO IV, COBOL, PASCAL PL/1, BASIC, ALGOL-68 etc.) were used during this generation.
The main features of third generation are −
- IC used
- More reliable in comparison to previous two generations
- Smaller size
- Generated less heat
- Faster
- Lesser maintenance
- Costly
- AC required
- Consumed lesser electricity
- Supported high-level language
Some computers of this generation were −
- IBM-360 series
- Honeywell-6000 series
- PDP (Personal Data Processor)
- IBM-370/168
- TDC-316
Fourth Generation of Computers: – The period of fourth generation: 1971-1980. VLSI microprocessor based.
The period of fourth generation was from 1971-1980. Computers of fourth generation used Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits. VLSI circuits having about 5000 transistors and other circuit elements with their associated circuits on a single chip made it possible to have microcomputers of fourth generation.

Fourth generation computers became more powerful, compact, reliable, and affordable. As a result, it gave rise to Personal Computer (PC) revolution. In this generation, time sharing, real time networks, distributed operating system were used. All the high-level languages like C, C++, DBASE etc., were used in this generation.
The main features of fourth generation are −
- VLSI technology used
- Very cheap
- Portable and reliable
- Use of PCs
- Very small size
- Pipeline processing
- No AC required
- Concept of internet was introduced
- Great developments in the fields of networks
- Computers became easily available
Some computers of this generation were −
- DEC 10
- STAR 1000
- PDP 11
- CRAY-1(Super Computer)
- CRAY-X-MP(Super Computer)
Fifth Generation of Computers: – The period of fifth generation: 1980-onwards. ULSI microprocessor based.
The period of fifth generation is 1980-till date. In the fifth generation, VLSI technology became ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology, resulting in the production of microprocessor chips having ten million electronic components.
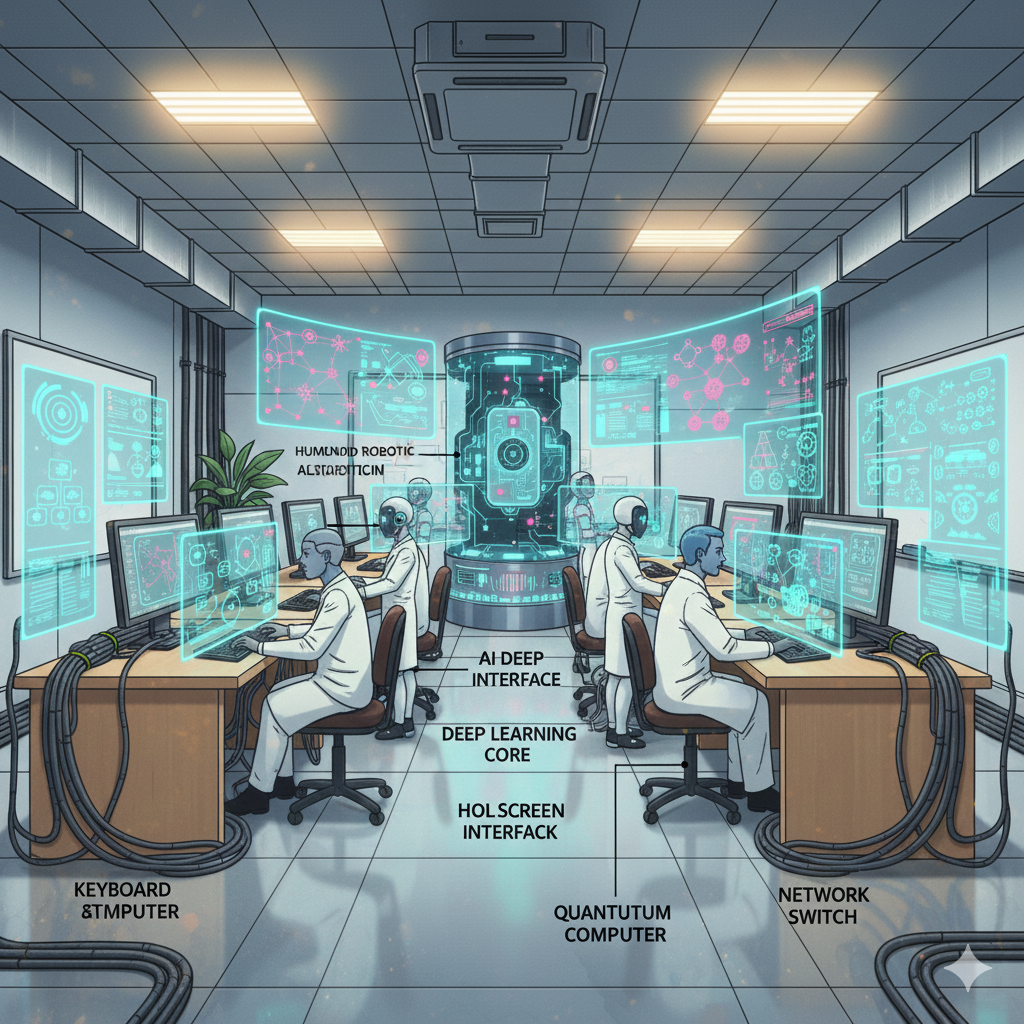
This generation is based on parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software. AI is an emerging branch in computer science, which interprets the means and method of making computers think like human beings. All the high-level languages like C and C++, Java, .Net etc., are used in this generation.
AI includes −
- Robotics
- Neural Networks
- Game Playing
- Development of expert systems to make decisions in real-life situations
- Natural language understanding and generation
The main features of fifth generation are −
- ULSI technology
- Development of true artificial intelligence
- Development of Natural language processing
- Advancement in Parallel Processing
- Advancement in Superconductor technology
- More user-friendly interfaces with multimedia features
- Availability of very powerful and compact computers at cheaper rates
Some computer types of this generation are −
- Desktop
- Laptop
- NoteBook
- UltraBook
- ChromeBook
| Generation | Period | Technology | Key Features | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | 1946–1959 | Vacuum Tube | Machine language, batch processing, huge, slow, expensive, generated heat | ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, IBM-701 |
| Second | 1959–1965 | Transistor | Smaller, reliable, faster, assembly & high-level languages | IBM 1620, IBM 7094, CDC 1604 |
| Third | 1965–1971 | Integrated Circuit (IC) | Smaller, reliable, ICs, high-level languages, multiprogramming | IBM-360 series, PDP, IBM-370 |
| Fourth | 1971–1980 | VLSI Microprocessor | PCs, portable, affordable, internet concept, time-sharing OS | DEC 10, STAR 1000, CRAY-1 |
| Fifth | 1980–Present | ULSI, AI | Parallel processing, artificial intelligence, natural language processing, multimedia | Desktop, Laptop, Notebook, Chromebook |
Generation refers to a change in technology used in computers. Five generations are recognized:
Conclusion
Computers have evolved rapidly from large vacuum-tube machines to modern AI-based systems. Understanding the types and generations of computers helps students learn how technology has developed and how computers are used in different fields today.
9. Applications of Computer
Computers are widely used in almost every field of modern life. They help humans perform tasks faster, more accurately, and efficiently. Below are the major applications of computers explained in detail.
1. Computers in Education
Computers play a very important role in the education sector.
- Used for online learning, virtual classes, and e-learning platforms
- Helpful in preparing notes, presentations, assignments, and projects
- Students use computers for research, exams, and skill development
- Teachers use computers for smart teaching and digital classrooms
Examples: Online courses, educational software, virtual labs.
2. Computers in Business
Computers are essential for business operations and management.
- Used for accounting, billing, payroll, and inventory management
- Help in data analysis, decision making, and record keeping
- Support online marketing, e-commerce, and customer management
- Increase productivity and reduce manual errors
Examples: Billing software, accounting tools, ERP systems.
3. Computers in Banking and Finance
Banks and financial institutions depend heavily on computers.
- Used for online banking, ATM services, and fund transfers
- Help in maintaining customer records and transaction history
- Enable digital payments, UPI, net banking, and mobile banking
- Improve security and speed of financial operations
Examples: ATM machines, banking software, payment gateways.
4. Computers in Healthcare
Computers have transformed the healthcare industry.
- Used to store patient records and medical history
- Help doctors in diagnosis, medical imaging, and lab testing
- Support online appointments and telemedicine
- Used in hospitals for billing and hospital management
Examples: Hospital management systems, MRI, CT scan machines.
5. Computers in Science and Research
Computers are very important in scientific research.
- Used for complex calculations and simulations
- Help in space research, weather forecasting, and data analysis
- Used to store and process large amounts of research data
- Improve accuracy and speed in experiments
Examples: Supercomputers used by ISRO and NASA.
6. Computers in Communication
Computers have made communication fast and easy.
- Used for email, video calls, messaging, and social media
- Enable global communication in real time
- Support online meetings and remote work
- Reduce distance barriers between people
Examples: Email services, video conferencing apps.
7. Computers in Entertainment
Entertainment industry uses computers widely.
- Used in movies, animation, gaming, and music production
- Enable video editing, graphic design, and special effects
- Provide access to online streaming platforms
- Help in creating digital art and media
Examples: Video games, OTT platforms, animation software.
8. Computers in Government Services
Governments use computers for public services.
- Used for record keeping, citizen data, and administration
- Support online services like Aadhaar, PAN, and online forms
- Improve transparency and efficiency
- Help in digital governance (e-Governance)
Examples: Online portals, digital ID systems.
9. Computers in Transportation
Computers help manage transportation systems.
- Used for traffic control and navigation
- Help in online ticket booking and scheduling
- Used in air traffic control and railway management
- Improve safety and efficiency
Examples: GPS systems, airline reservation systems.
10. Computers in Daily Life
Computers are part of everyday life.
- Used for shopping, bill payments, and online services
- Help in learning new skills and accessing information
- Used in homes for entertainment and communication
- Save time and effort in daily tasks
Examples: Smartphones, laptops, smart devices.
Conclusion
Computers have become an essential part of modern society. From education to healthcare, business to entertainment, computers help improve efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. Life without computers is almost impossible in today’s digital world.







